ChatGPT's Impact on Critical Thinking: A Comprehensive Analysis of MIT's Groundbreaking Neuroscience Study
Comprehensive infographic summarizing MIT study on ChatGPT's impact on brain function and learning
The integration of artificial intelligence tools in educational settings has reached a critical juncture, with profound implications for human cognitive development and learning processes. Recent research from MIT's Media Lab has unveiled concerning evidence about how AI assistance, particularly ChatGPT, may be fundamentally altering brain function and undermining essential cognitive skills in students and young adults
Study Overview and Methodology
Research Design and Participants
Dr. Nataliya Kosmyna and her team at MIT Media Lab conducted a comprehensive four-month longitudinal study examining the neural and behavioral consequences of large language model (LLM) assistance during essay writing tasks 23. The research involved 54 participants aged 18-39 from the Boston area, representing a critical demographic of young adults whose cognitive patterns are still developing and potentially malleable 14.
The experimental design employed sophisticated electroencephalography (EEG) technology to monitor brain activity across 32 neural regions while participants engaged in SAT-style essay writing tasks 23. This neuroimaging approach provided unprecedented insights into real-time cognitive engagement and neural connectivity patterns during learning activities 56.
Experimental Groups and Conditions
The study divided participants into three distinct experimental conditions that reflected common approaches to information processing and learning in contemporary educational environments 23:
Brain-Only Group: Participants relied solely on their cognitive resources without any external technological assistance, representing traditional learning approaches that emphasize internal mental processing and memory retrieval 12.
Search Engine Group: Participants utilized Google search functionality to gather information and support their essay writing, mirroring conventional research methodologies that encourage active information seeking and evaluation 23.
ChatGPT Group: Participants used OpenAI's ChatGPT for various aspects of essay composition, from idea generation to content refinement, representing the emerging trend of AI-assisted learning and content creation 12.
The research methodology included a crucial fourth session where participants switched conditions, allowing researchers to examine both immediate and residual effects of different technological interventions on cognitive performance 23.
Neural Activity and Brain Connectivity Findings
EEG Brain Wave Analysis
The study's most significant contributions emerged from detailed analysis of brain wave patterns across different frequency bands, each associated with specific cognitive functions and learning processes 267. The EEG data revealed systematic differences in neural engagement that corresponded directly to the level of external technological assistance provided 25.
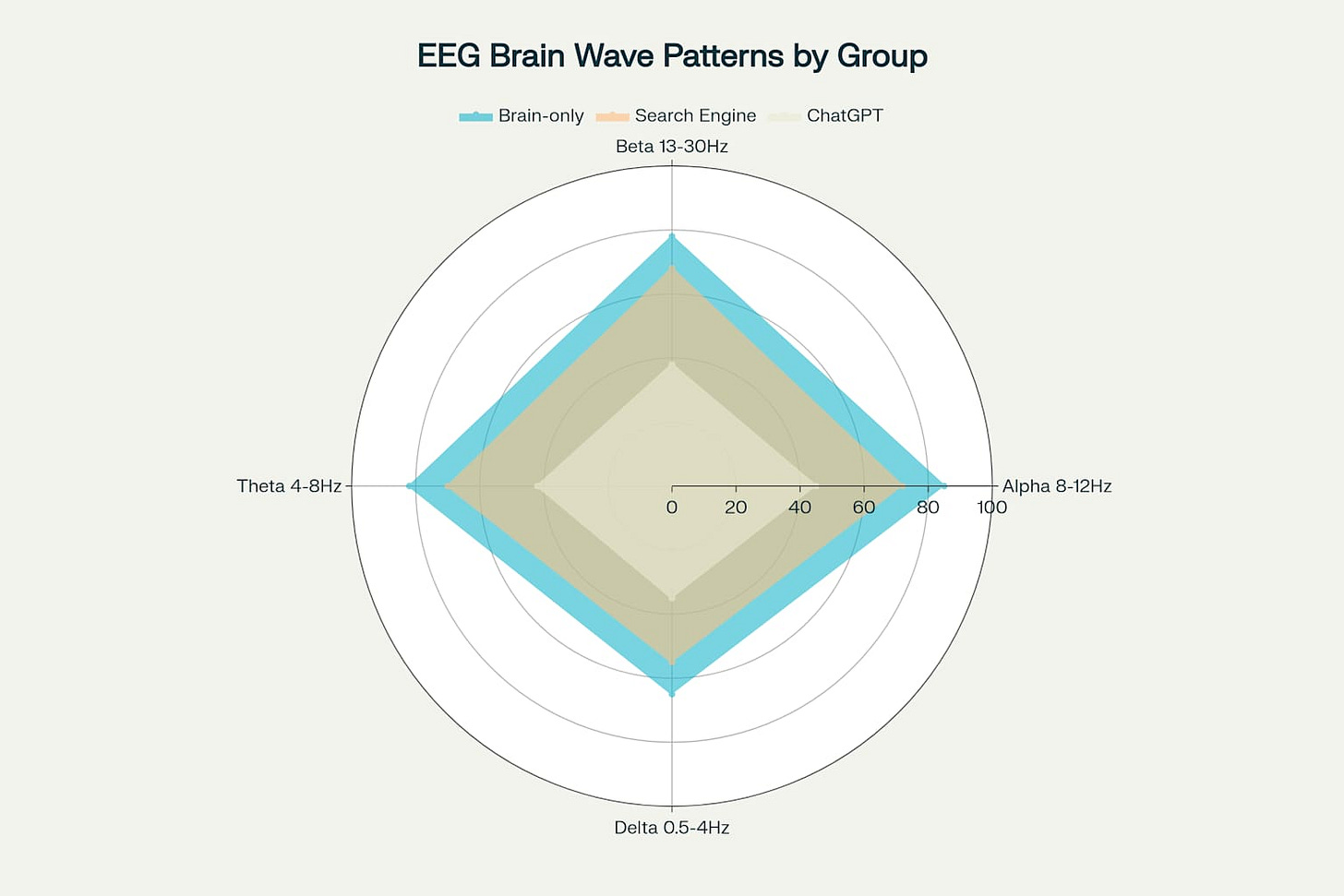
Alpha waves (8-12 Hz), traditionally associated with creativity, ideation, and relaxed focus, showed marked variations across experimental groups 67. Brain-only participants demonstrated strong alpha activity (85 relative units), while ChatGPT users exhibited significantly diminished alpha patterns (45 relative units), suggesting compromised creative and ideational processes 26.
Beta waves (13-30 Hz), linked to active concentration and problem-solving activities, followed similar patterns of decline with increased AI assistance 67. The brain-only group maintained robust beta activity (78 relative units) compared to the substantially weakened beta patterns in ChatGPT users (38 relative units) 26.
Theta waves (4-8 Hz), crucial for memory formation and deep cognitive processing, revealed perhaps the most concerning disparities 68. These waves, essential for consolidating information into long-term memory, were significantly stronger in brain-only participants (82 relative units) compared to ChatGPT users (42 relative units) 26.
Brain Connectivity Patterns
The research uncovered fundamental differences in neural connectivity patterns that scaled systematically with the degree of external technological support 25. Brain connectivity analysis revealed that cognitive activity diminished proportionally to the level of external tool assistance, with profound implications for learning and memory formation 28.
Brain-only participants exhibited the strongest and most distributed neural networks, characterized by robust connections between frontal-parietal regions and widespread cortical activation 25. These connectivity patterns are essential for executive function, working memory, and the integration of new information with existing knowledge structures 58.
Search engine users demonstrated intermediate connectivity levels, maintaining substantial neural engagement while benefiting from external information access 25. This group showed activation patterns similar to brain-only participants, particularly in regions associated with visual processing and information evaluation 25.
ChatGPT users displayed the weakest overall neural coupling, with significantly reduced connectivity across all measured brain regions 25. This finding suggests that AI assistance may bypass critical neural pathways involved in deep learning and memory consolidation 28.
Performance Metrics and Behavioral Outcomes
Cognitive Engagement and Learning Satisfaction
The study employed multiple assessment methodologies to evaluate learning outcomes, including human teacher evaluations, AI-based scoring systems, and self-reported measures of satisfaction and ownership 23. These comprehensive assessments revealed systematic differences in learning quality and student engagement across experimental conditions 12.
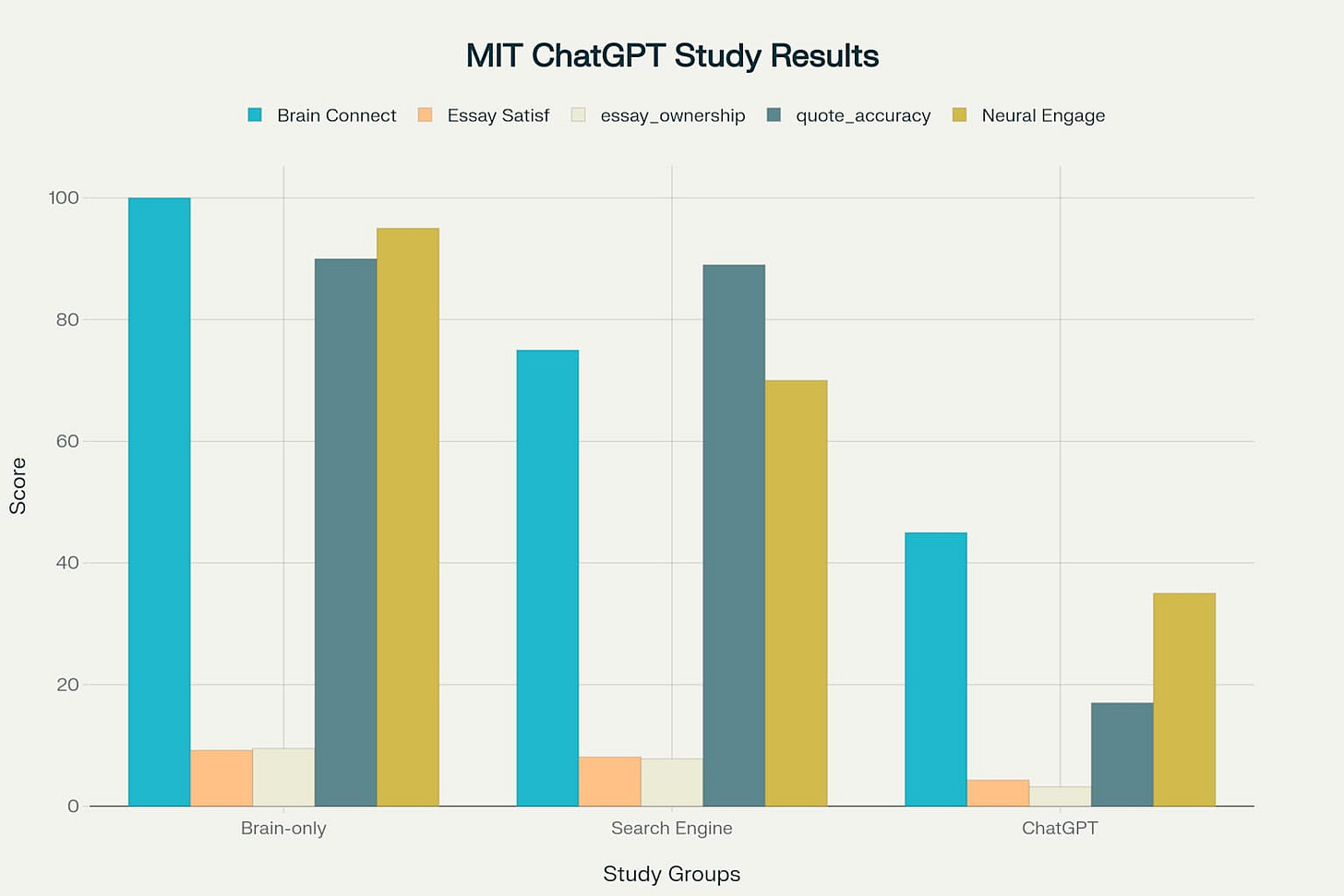
Essay satisfaction ratings demonstrated clear patterns of decline with increased AI assistance, with brain-only participants reporting high satisfaction levels (9.2 out of 10) compared to dramatically lower satisfaction among ChatGPT users (4.3 out of 10) 12. These findings suggest that AI assistance may undermine intrinsic motivation and personal investment in learning activities 910.
Ownership feelings followed similar patterns, with brain-only participants expressing strong personal connection to their work (9.5 out of 10) while ChatGPT users reported minimal sense of authorship (3.2 out of 10) 12. This erosion of intellectual ownership has significant implications for student engagement and long-term learning motivation 910.
Memory Consolidation and Recall Abilities
One of the study's most striking findings involved participants' ability to recall and quote from essays they had written just minutes earlier 12. This memory assessment provided direct evidence of information processing and consolidation differences across experimental groups 116.
Brain-only participants demonstrated excellent recall abilities, with 90% successfully quoting from their recent work 12. Search engine users maintained similar recall performance (89%), suggesting that active information seeking does not impair memory consolidation 12.
ChatGPT users showed dramatically impaired recall abilities, with only 17% able to accurately quote from their own essays 12. This finding indicates that AI assistance may interfere with fundamental memory processes essential for learning and knowledge retention 116.
Longitudinal Effects and Cognitive Degradation
Progressive Performance Decline
The study's longitudinal design revealed concerning trends in cognitive engagement and performance over the four-month research period 12. These temporal patterns provided crucial insights into the cumulative effects of AI assistance on learning behaviors and cognitive development 1213.
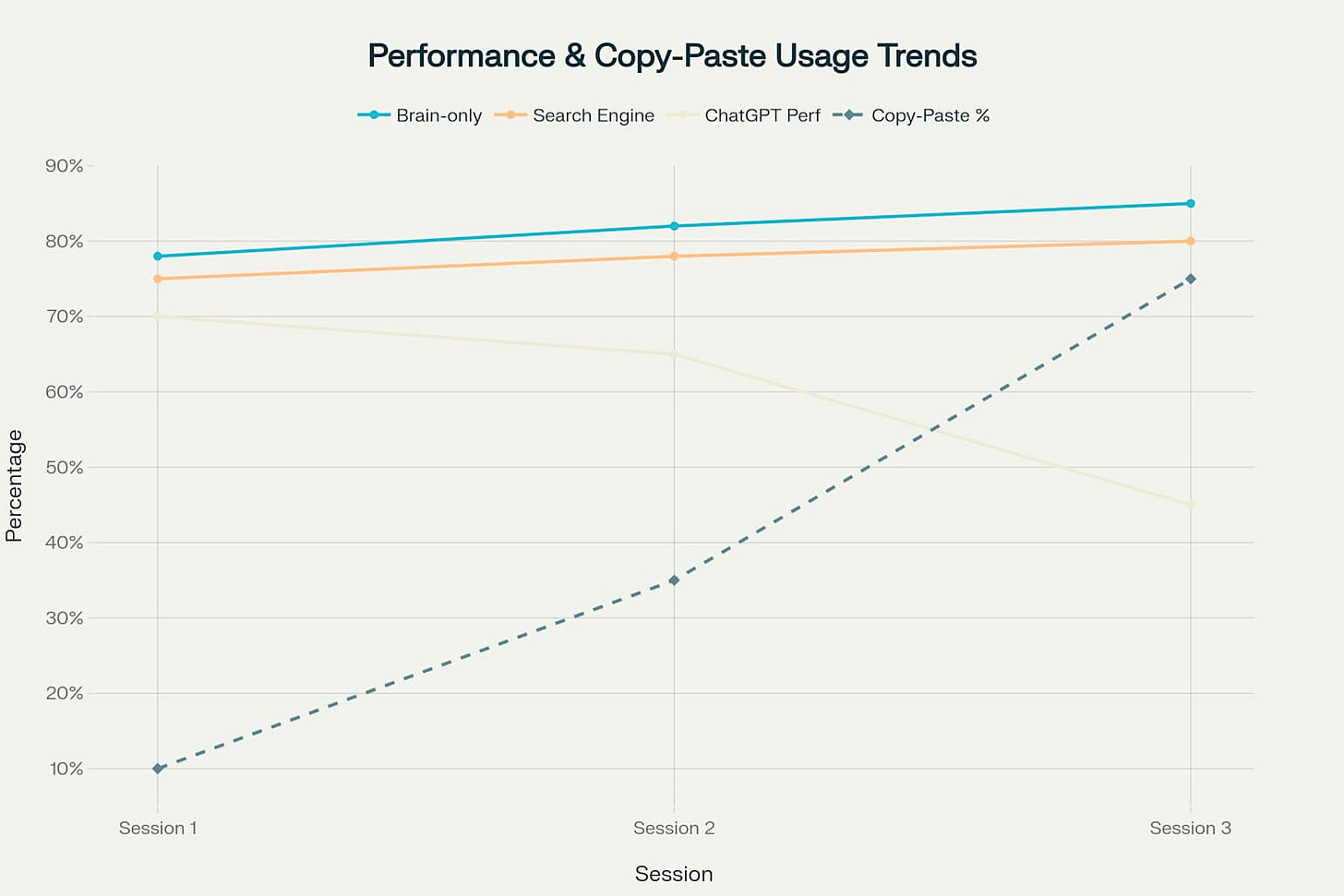
Session-by-session analysis demonstrated divergent performance trajectories across experimental groups 212. Brain-only participants showed steady improvement, with performance increasing from 78% in session one to 85% in session three 12. Search engine users also demonstrated consistent improvement, progressing from 75% to 80% over the study period 12.
ChatGPT users exhibited the opposite pattern, with performance declining from an initial 70% to a concerning 45% by session three 12. This degradation coincided with dramatically increased reliance on copy-paste behaviors, rising from 10% in session one to 75% in the final session 12.
Cognitive Debt Accumulation
The research introduced the concept of "cognitive debt," representing the cumulative cost of outsourcing mental processes to AI systems 29. This phenomenon manifested as progressive disengagement from cognitive effort and increasing dependence on artificial assistance 910.
Participants who initially used ChatGPT and then switched to brain-only conditions in session four showed persistent cognitive deficits 212. These individuals demonstrated reduced alpha and beta connectivity patterns, indicating lasting neural changes from AI exposure 26.
Conversely, brain-only participants who gained access to ChatGPT in session four showed enhanced performance and maintained strong neural connectivity patterns 212. This finding suggests that establishing strong cognitive foundations before AI assistance may preserve learning capabilities 1210.
Educational Implications and Systemic Concerns
Impact on Developing Minds
The study's findings carry particular significance for educational policy and practice, especially given the rapid adoption of AI tools in academic settings 113. Dr. Kosmyna expressed urgent concern about potential implementation of AI systems in early childhood education, warning that "developing brains are at the highest risk" 112.
The research suggests that AI assistance during formative learning experiences may interfere with the development of essential cognitive skills 1310. These include critical thinking, creative problem-solving, memory consolidation, and independent reasoning abilities that form the foundation of intellectual development 1310.
Educational institutions face complex decisions about balancing AI's potential benefits with preservation of human cognitive capabilities 1014. The study's findings suggest that timing and methodology of AI integration may be crucial factors in determining educational outcomes 1210.
Long-Term Cognitive Consequences
The research raises concerns about potential long-term effects of widespread AI adoption in educational contexts 139. Extended reliance on AI assistance may contribute to cognitive atrophy, reduced intellectual independence, and diminished creative thinking capabilities 1310.
Professional implications extend beyond academic settings, with potential impacts on workforce capabilities and innovation capacity 1213. The study's findings about reduced problem-solving abilities and creative thinking may have significant economic and societal consequences 1310.
Recommendations for Balanced AI Integration
Educational Best Practices
Based on the study's findings, several strategies emerge for responsible AI integration in educational settings 1014. These approaches emphasize preserving human cognitive development while leveraging AI's potential benefits 1210.
Sequential Learning Approaches: The research suggests that students should master foundational cognitive skills before accessing AI assistance 1210. This "brain-first" methodology may preserve essential neural pathways while allowing students to benefit from AI capabilities 212.
Hybrid Learning Models: Combining traditional cognitive exercises with carefully structured AI assistance may optimize learning outcomes 1014. These approaches should emphasize active student engagement and critical evaluation of AI-generated content 1210.
Metacognitive Skill Development: Teaching students to assess AI outputs and maintain awareness of their own thinking processes may help preserve critical thinking abilities 1014. These skills are essential for navigating an AI-enhanced educational landscape 1310.
Policy and Implementation Considerations
The study's pre-publication release reflects urgent concerns about premature AI deployment in educational settings 14. Policymakers must carefully consider the cognitive implications of AI integration before implementing widespread technological changes 110.
Comprehensive research protocols should evaluate both immediate and long-term effects of AI assistance on student learning and development 212. These assessments must include neurological, behavioral, and academic outcome measures 210.
Professional development programs should prepare educators to implement balanced AI integration strategies that preserve human cognitive development 1014. These programs must emphasize the importance of maintaining student cognitive engagement and intellectual independence 1210.
Study Limitations and Future Research Directions
Current Research Constraints
The MIT study, while groundbreaking, acknowledges several limitations that affect the generalizability of its findings 23. The relatively small sample size (54 participants) and geographic concentration (Boston area) may limit the applicability of results to broader populations 212.
The research focused specifically on ChatGPT, and findings may not extend to other AI models or technological tools 212. Future research should examine various AI systems to understand the broader implications of artificial intelligence assistance 1215.
The study's concentration on essay writing tasks may not reflect the full spectrum of AI applications in educational settings 215. Research examining diverse academic tasks and subject areas would provide more comprehensive insights 1514.
Future Research Priorities
Longitudinal studies examining AI's effects on children and adolescents represent a critical research priority 112. These investigations should track cognitive development over extended periods to understand long-term implications 129.
Cross-cultural research could provide insights into how different educational systems and cultural contexts influence AI's impact on learning 1215. Such studies would help identify universal principles and culturally specific considerations 1514.
Intervention research should explore strategies for mitigating negative AI effects while preserving beneficial applications 1210. These studies could inform evidence-based guidelines for educational AI implementation 1014.


